Building data-driven React applications with Relay
9 october 2019

Aurélien David
- CTO at Cap Collectif
- Former JoliCode guy



collective intelligence driven civic start-up that develops participatory applications.

- 23 people 🏃
- 8 devs 👩💻





Consultation
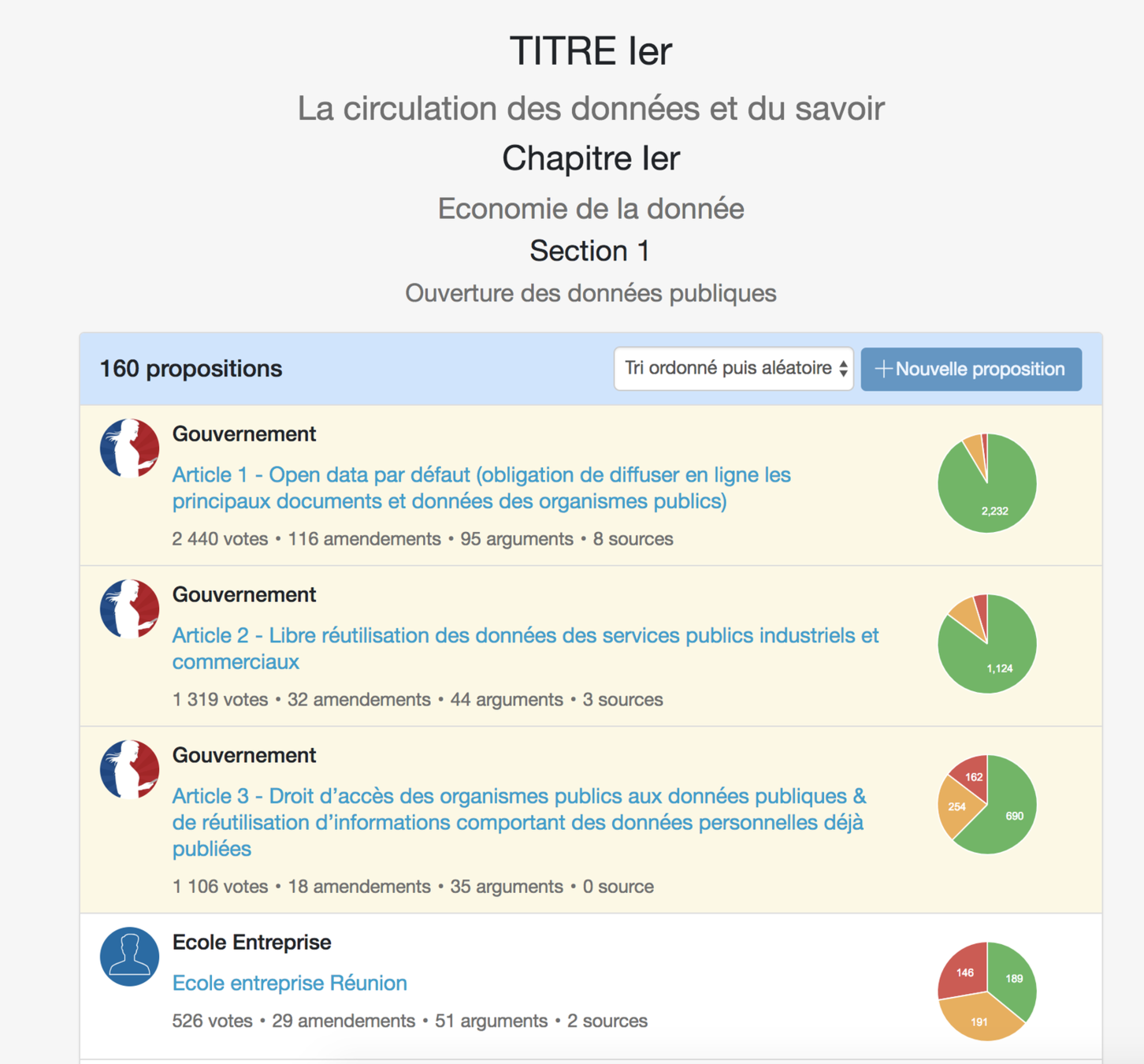
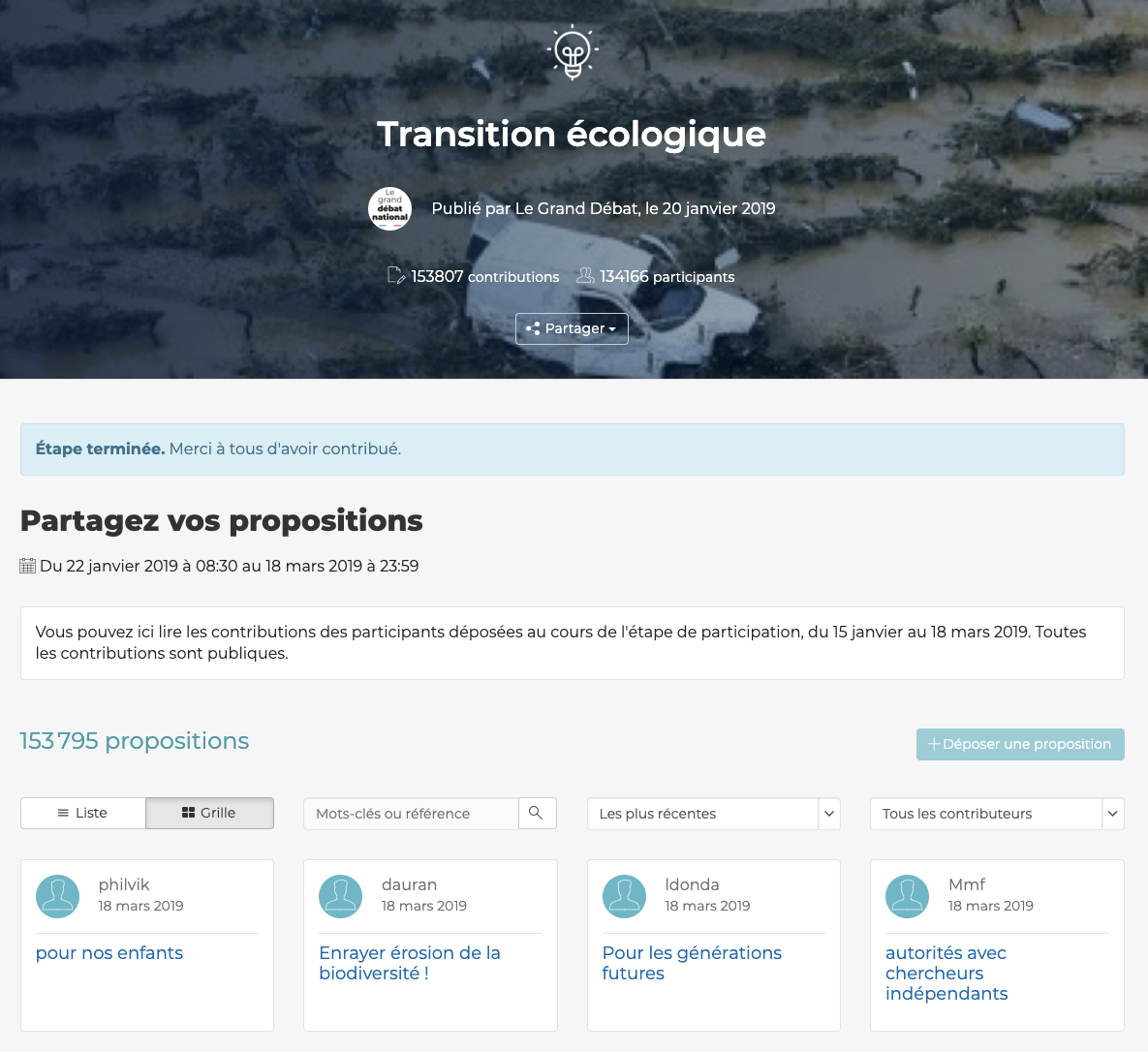
🇫🇷 Le Grand Débat National
+ 1,9 M
Contributions
+ 10 000
Local events
+ 2,7 M
Visitors
Data fetching is hard
Over-fetching
Under-fetching
Requests waterfall
What we tried
- Using fetch in componentDidMount 😀
- More and more REST endpoints 😐
- Multiple components, multiple requests 🥺
- Share data in a Flux store 🤔
- Dispatch redux actions, for loading, success, failures 😨
- Redux-saga boilerplate… 😱
☠️
Allows clients to ask what they want.
Easily aggregate data from multiple sources.
Uses a type system to describe the data.

GraphQL clients for Frontend



API → props
Declarative Data-Binding
Declare the data your components need with GraphQL, Relay determines how and when to fetch your data.

Colocation
GraphQL is written next to the views that rely on them. Relay aggregates queries into efficient network requests.


Mutations
Write GraphQL mutations and Relay offers automatic data consistency, optimistic updates, and error handling.

Relay Specification
Global Object Identification
A mechanism for storing and refetching an object.
Connections
Consistent abstractions for bi-directional pagination.
Input Object Mutations
Structure around mutations to make them predictable.
A set of 3 additional conventions to adopt on a GraphQL server.
Text
import {createFragmentContainer, graphql} from 'react-relay';
class UserAvatar extends React.Component {
render() {
const { user } = this.props;
return (
<img alt={user.username} src={user.avatarUrl} />
);
}
}
export default createFragmentContainer(UserAvatar, {
user: graphql`
fragment UserAvatar_user on User {
username
avatarUrl
}
`,
});Use fragments everywhere and Relay will make sure every components has the data that they need. 👍
Data requirements are colocated with components.
Relay uses data masking (each component only see what it asked for), it improves reusability, refactoring and deleting code.
<ComponentFileName>_<propName>
UserAvatar_user
🔥 Fragments Containers.
🔥 Composing Fragments
class UserProfile extends React.Component {
render() {
const {user} = this.props;
return (
<div>
<span>Inscrit le {user.createdAt}</span>
<UserAvatar user={user} />
</div>
);
}
}
export default createFragmentContainer(UserProfile, {
user: graphql`
fragment UserProfile_user on User {
createdAt
...UserAvatar_user
}
`,
});Other Types of Fragment Containers
- createPaginationContainer - a container that will refetch data based on pagination
Automate the boring pagination logic, only provides a loadMore method.

Other Types of Fragment Containers
- createRefetchContainer - a container that has a refetch query to get more data afterwards
For all other use cases:
sorting, filtering, loading more details, refreshing…
Provides a refetch method.
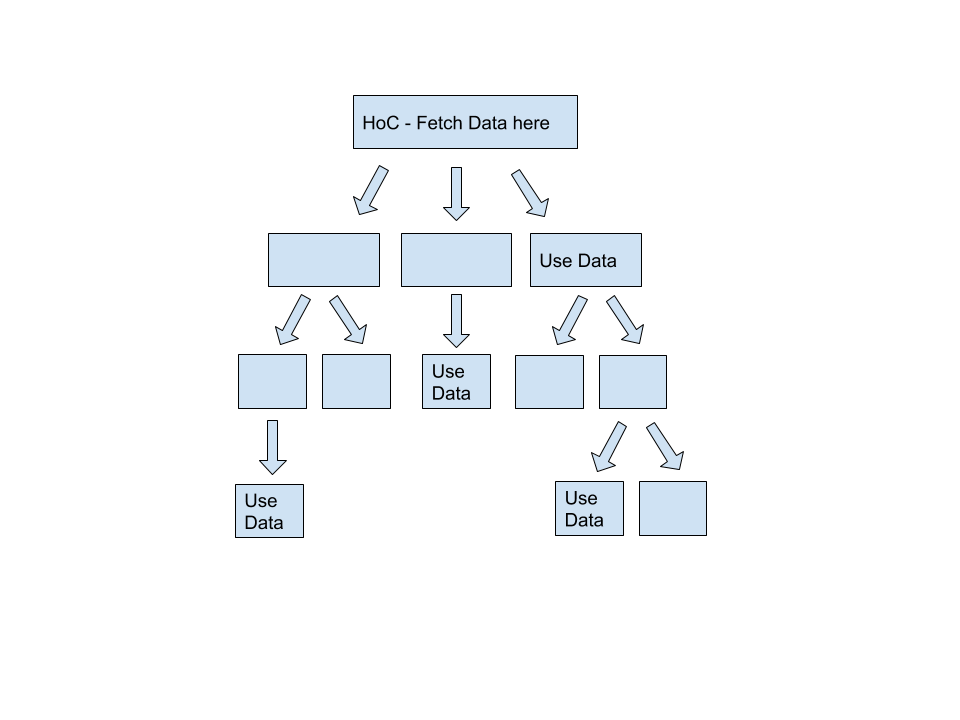
When is the API called ?
A Relay app always starts with a QueryRenderer and a tree of containers either fragments, refetch or pagination.
QueryRenderers can be rendered anywhere that a React component can be rendered.
import React from 'react';
import {graphql, QueryRenderer} from 'react-relay';
import { environment } from './environment';
import UserProfile from './UserProfile';
const App = () => (
<QueryRenderer
environment={environment}
query={graphql`
query ViewerQuery {
viewer {
...UserProfile_user
}
}
`}
variables={{}}
render={({error, props}) => {
if (error) {
return <div>Error!</div>;
}
if (!props) {
return <div>Loading...</div>;
}
return <UserProfile user={props.viewer} />;
}}
/>
);
Relay QueryRenderer
QueryRenderer will fetch GraphQL data and pass that to render props.
QueryRenderer handles the state for loading, success and failure. 👌
It needs a Relay Environment which bundles together the configuration, cache storage, and network-handling that Relay needs in order to operate. ⚙️
Relay Store

The Relay Store is how Relay stores data of all fragments and queries. All records/nodes are normalized in the store, this is why we need a unique and global ID for each record.
Mutations
const mutation = graphql`
mutation AddCommentVoteMutation(
$input: AddCommentVoteInput!
) {
addCommentVote(input: $input) {
voteEdge {
node {
id
contribution {
id
viewerHasVote
}
}
}
}
}
`;Mutations
const variables = { commentId: '1234'};
const onCompleted = () => { console.log('Done !') };
commitMutation(environment, {
mutation,
variables,
onCompleted,
})Relay will automatically update the fields on the records referenced in the mutation response (using ids).
Relay re-renders live components with data updates.
You can also use an updater function for complex cases, or avoiding to ask a huge mutation payload.
Use commitMutation to create and execute mutations.
Optimistic UI
const optimisticResponse = {
addCommentVote: {
voteEdge: {
node: {
contribution: {
id: variables.input.commentId,
viewerHasVote: true
}
}
}
}
}You can also use an optimisticUpdater function for complex cases.
Update the store before the mutation request has completed.
Local Updates
commitLocalUpdate(environment, store => {
const dataID = this.props.comment.id;
// Update a value from store
const commentProxy = store.get(dataID);
commentProxy.setValue(new DateTime(), 'deletedAt');
// Or delete node form the store
store.delete(dataID);
});How to replace Redux with Relay
Relay Compiler and Babel Plugin
The Relay compiler validates your queries against your GraphQL schema and enforces strict naming.
It will optimise all your queries and fragments, so you can have a great DX without losing performance 🔥
It emits types for your fragment's fields selections and queries variables and responses.
Relay compiler plugins (typescript, flow and reasons) support
100% type-safe application code
import type { ExampleFragment_artist }
from "__generated__/ExampleFragment_artist.graphql"
const component = (props: { artist: ExampleFragment_artist }) => (
<div>About the artist: {props.artist.biography}</div>
);
export const ExampleFragment = createFragmentContainer(
component,
{
artist: graphql`
fragment ExampleFragment_artist on Artist {
biography
}
`
}
)❤️ without the maintenance cost ❤️
Want more features ?
- include and skip directives
- persisted queries
- Subscriptions
Relay Roadmap
Relay vs Apollo
-
Heavily based on conventions
- enforce a very clean architecture
- help devs to build scalable codebases
- Facebook support and OSS community
- Relay and React teams lives besides one another
- Facebook-scale best-practices (8+ years of GraphQL)
- Compile-time query generation (removing runtime overhead)
Destroying the "Relay is hard" myth
Relay is an opinionated framework for building user interfaces.
Learning Relay
- Documentation is great, checkout : relay.dev
- Code examples : relayjs/relay-examples
- #relay on GraphQL slack
- Relay Development Tools (relayjs/relay-devtools)
- ESLint plugin (relayjs/eslint-plugin-relay)
Amazing Frontend Developer Experience
😍 Remove most of data fetching code.
🚆 Optimistic UI and cached data.
✅ Generate Flow/Typescript typings using the strongly-typed schema.
Thanks !
Any questions ?

We work hard to update our democracy (with Relay)… 👍
Slides: spyl.net/slides/mobitalk-2019